Introduction
The aroma of an agarbatti incense stick is a familiar scent in many households, temples, and meditation spaces. But have you ever wondered how your nose picks up this distinct smell? Understanding the science behind it can be fascinating. In this article, we’ll delve into the mechanics of how we detect the smell of an agarbatti incense stick.

The Anatomy of Smell
Before we get into the specifics of agarbatti, let’s first understand how our sense of smell works. Our nose is equipped with olfactory receptors that detect various odor molecules in the air. When you light an agarbatti, it releases these molecules, which then travel to your nose.
“I remember the first time I walked into a yoga studio and was immediately enveloped by the soothing scent of agarbatti. It was a transformative experience that led me to explore the science behind how our noses and brains work together to detect such unique aromas.”
The Role of Olfactory Receptors
Olfactory receptors are specialized cells in the nose that bind to odor molecules. When these receptors detect a specific molecule, they send signals to the brain. Your brain then interprets these signals as a particular smell.

The Chemical Composition of Agarbatti
Agarbatti incense sticks are made from a blend of natural and synthetic ingredients. These can include resins, essential oils, and aromatic herbs. When burned, these ingredients undergo a chemical reaction that releases various types of odor molecules.
The Release of Odor Molecules
As the agarbatti burns, it emits a complex mixture of molecules. These include aromatic compounds that are specifically designed to be pleasant and calming. The heat from the burning process helps disperse these molecules into the air, making it easier for them to reach your olfactory receptors.
The Journey of an Odor Molecule
Once released, the odor molecules from the agarbatti travel through the air. They may diffuse through a room, carried by air currents. Eventually, these molecules reach your nose, where they bind to your olfactory receptors.
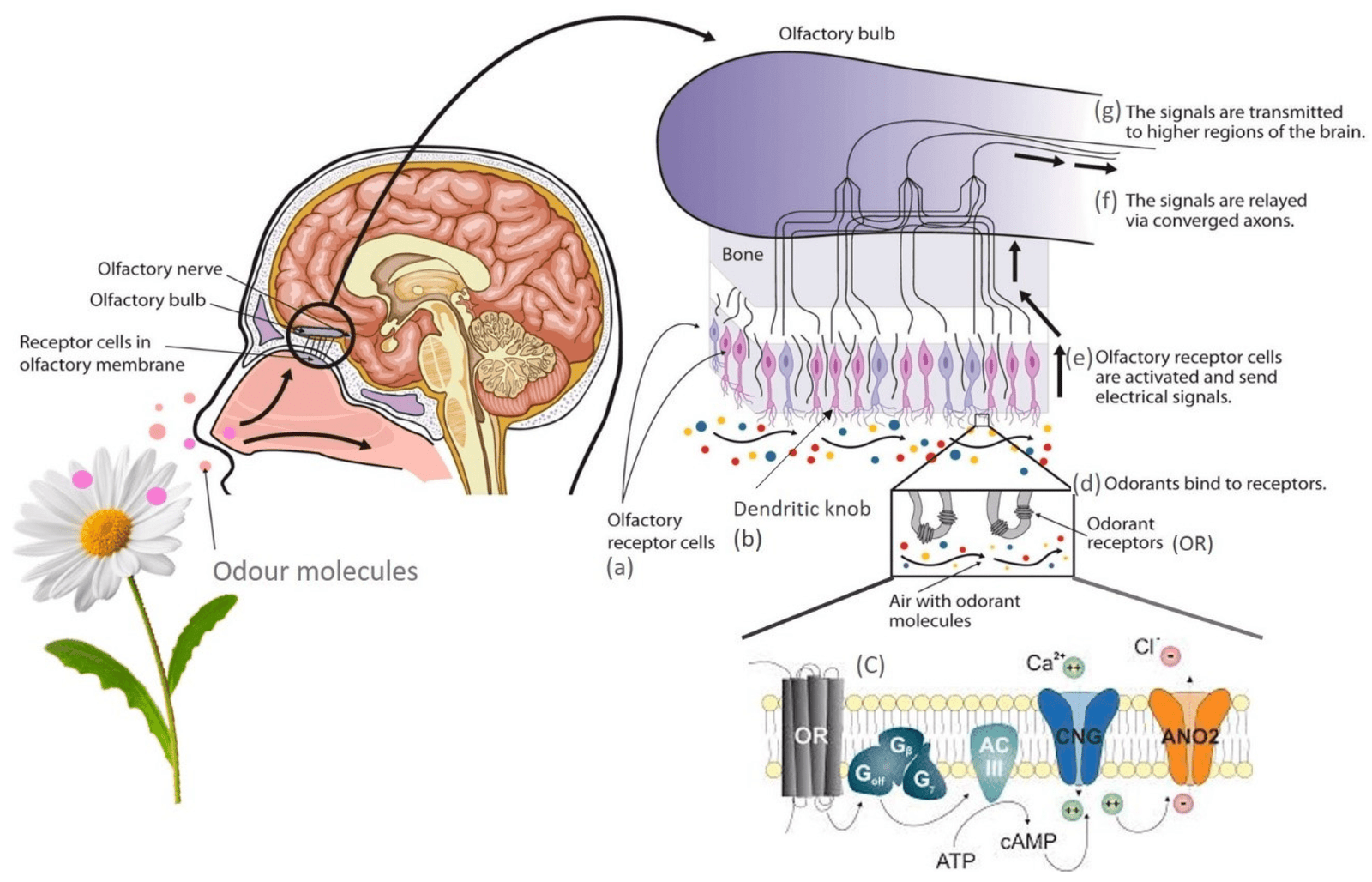
Signal Transmission to the Brain
Upon binding to the receptors, a signal is sent to the olfactory bulb in the brain. This area processes the information and passes it on to other regions responsible for memory and emotion. That’s why the smell of agarbatti can often evoke strong feelings or memories.
The Final Interpretation
Your brain combines all this information to identify the smell as coming from an agarbatti. This entire process happens in a matter of seconds, allowing you to enjoy the soothing aroma almost instantly after lighting the incense stick.
“The use of agarbatti dates back to ancient civilizations, where it was used in religious ceremonies and medicinal practices. Back then, people believed that the scent had the power to ward off evil spirits. While we now understand the science behind the smell, the cultural significance of agarbatti remains strong.”
Why Some People Perceive Smells Differently
It’s worth noting that not everyone interprets the smell of agarbatti in the same way. Genetic factors can influence how your olfactory receptors are shaped, affecting how you perceive various odors. Cultural and personal experiences also play a role in how a smell is interpreted.
Conclusion
To detect the smell of an agarbatti incense stick you go through a complex process consisting of multiple steps. From the release of odor molecules to the interpretation by the brain, each stage is crucial for us to identify and enjoy this unique aroma. So the next time you light an agarbatti, you’ll have a deeper appreciation for the intricate science that allows you to experience its calming scent.




